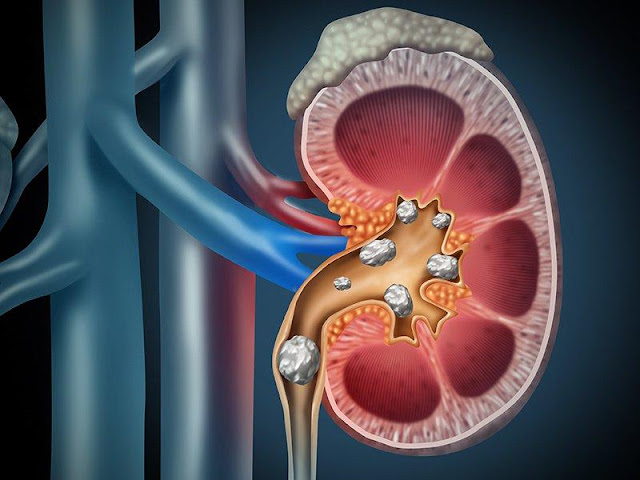
To visualize and remove kidney stones simultaneously, a fiberoptic endoscope called a Urolithiasis Management Device is used.
Shock wave lithotripters are minimally invasive or non-invasive kidney stone treatment tools. These tools produce shockwaves that are concentrated on the calculi and can break up stones of different sizes. A fiberoptic endoscope called a ureterorenoscopy is used in a minimally invasive procedure to simultaneously visualize and remove kidney stones. With a higher rate of stone removal success, it is more dependable.
The term
"urolithiasis" refers to the formation of stones in the urinary
system. Nephrolithiasis, or the development of kidney stones, Ureterolithiasis,
or the formation of stones in the ureters, and cystolithiasis, or the
development of stones in the bladder, are the three different types of
urolithiasis. One of the most prevalent lifestyle disorders and a significant
current healthcare issue is stone formation. The European Association of
Urology estimates that kidney stones affect about 10% of the world's
population. Additionally, this disorder has a lifetime recurrence rate of about
50%. One of the key factors driving an increase in demand for these services is
the rising prevalence and incidence rates of urinary stones combined with the
growing preference for minimally invasive surgeries worldwide.
According to where the
stones form, Urolithiasis
Management Devices is a term used to
describe the development of stones in the urinary system. One of the most
prevalent chronic disorders and a current major health concern is
nephrolithiasis, which is the development of kidney stones. The European
Association of Urology estimates that urolithiasis affects about 10% of people
worldwide. Additionally, the lifetime recurrence rate of this nephrolithiasis
disorder is close to 50%.
The term Urolithiasis Management Devices refers
to calculi or stones that develop in the urinary tract. The urinary system,
usually the kidneys or ureters but also the bladder and/or urethra, develops
calcifications as a result of this condition.
A common condition,
urolithiasis has a number of risk factors and causes, including lifestyle
choices and other practises.
Although some people do
not experience symptoms, kidney stones are a common health issue; in fact, it
is estimated that up to 10% of all people will develop one at some point in
their lifetime. Every year, urolithiasis causes about 1 in 1,000 patients to be
hospitalised.



Comments
Post a Comment